

Over a decade ago we added the Focused Spleen to our AFAST® Protocol because splenic disease is common in our small animal patients, and as a result of the discovery of “anaphylactic medically-treated hemoabdomen” in dogs, first reported by the author, and a MUST watch FASTVet Webinar here. The Focused Spleen is another FASTVet original for point-of-care ultrasound.
The AFAST® followed by the Focused Spleen. When your patient is in RIGHT lateral recumbency or standing, AFAST® is performed by imaging in the same standardized order of the DH view, followed by the SR view (least gravity-depender), the CC view and then ending at the most gravity-dependent view, now renamed more accurately, the Spleno-Intestino Umbilical (SIU) view. The SIU is performed at the level of the umbilicus and directing the scanning plane into the AFAST®’s most gravity-dependent pouch called the “Umbilical Pouch” followed by the Focused Spleen. These first 4 views – DH, SR, CC, SIU – make up the AFAST® Abdominal Fluid Scoring System.
The Focused Spleen is performed by tracking the spleen after the SIU view. Then the spleen is followed by “sliding and fanning cranially and caudally” following a reference point that helps overlap sections being fanned (interrogated). Really fan to maximize the amount of spleen being imaged because as the author says, “Never trust the tricky spleen.” Sweeping dorsally along the body wall, and repeating the same “sliding and fanning cranially and caudally imaging technique” until the spleen is tracked to the left kidney at the SR view. Fanning and changing the depth on the screen using the “AFAST Target-organ 50% Rule” is important to interrogate as much of the splenic parenchyma as possible with this screening test.
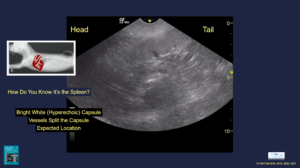
The Spleen is identified by the following:
- Its bright white hyperechoic capsule (unlike the liver whose capsule is not sonographically distinct in normalcy)
- Its vessels split the capsule (unlike the liver blood supply)
- Its expected anatomical location
Common Splenic Abnormalities:
- Any mass that deforms the capsule of the spleen is a serious finding
- Severe splenomegaly with a bright white (hyperechoic) Swiss cheese or moth-eaten appearance R/O lymphoma
- Severe splenomegaly with a dark (hypoechoic) Swiss cheese or moth-eaten appearance R/O splenic torsion (apply color flow Doppler)
Some other Quick Facts:
- The dog spleen should not extend to a small sized urinary bladder (however, consider the effects of sedation)
- The dog spleen may fold on itself in normalcy
- The cat spleen should never folds on itself and should be less than 10mm in thickness
Our 2nd edition of our textbook Point-of-care Ultrasound Techniques, Wiley ©2021 has updates on the Focused Spleen and its common abnormalities that you may learn. Send your comments to Dr. Greg Lisciandro at LearnGlobalFAST@gmail.com
gl/GL 1-21-2025