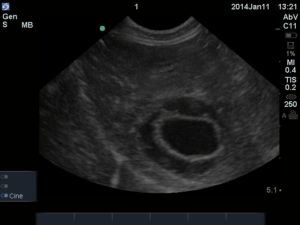
Fig. 1: The classic starting point and depth at the AFAST DH view. Note the thin white (hyperechoic)line that represents the typical unremarkable gallbladder wall; and that adequate depth beyond the diaphragm allows the surveillance for pericardial effusion, the other major rule out to anaphylaxis in collapsed dogs for the gallbladder halo sign.
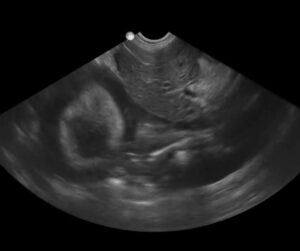
The sonographic finding of the gallbladder halo sign has been reported to be helpful as a marker for anaphylaxis (AX) in dogs since their shock organ (where most mast cells reside) is their liver and gastro-intestinal tract (unlike humans and cats that have the lungs as their shock organ). The massive histamine release causes acute hepatic congestion due to constriction of hepatic venous outflow (Quantz, JVECC 2009). Of course, other signs are helpful for the diagnosis of AX including acute gastrointestinal signs (vomiting and defecating) with collapse, an elevated lactate, an elevated alanine transaminase (ALT). and hemoconcentration. The image below shows a massive gallbladder halo sign at the AFAST DH view at triage (within minutes of patient arrival). In the following image, you can clearly see pericardial effusion surrounding the heart as imaged at the DH view. Take our AFAST Course to learn more; link for more information- Learn more about AFAST!